 Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, [12] also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. [3] . It is usually associated with developmental delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic physical features. [1][13]
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, [12] also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. [3] . It is usually associated with developmental delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic physical features. [1][13] Down syndrome varies in severity among individuals. The condition causes lifelong intellectual disability and developmental delays. It's the most common genetic chromosomal cause of intellectual disabilities in children. It also commonly causes other medical conditions, including heart and digestive system problems.
Down syndrome varies in severity among individuals. The condition causes lifelong intellectual disability and developmental delays. It's the most common genetic chromosomal cause of intellectual disabilities in children. It also commonly causes other medical conditions, including heart and digestive system problems. Down syndrome is a genetic condition where a person is born with an extra chromosome. This can affect how their brain and body develop. People diagnosed with Down syndrome can lead healthy lives with supportive care. Down syndrome is a condition in which a person has an extra copy of chromosome 21.
Down syndrome is a genetic condition where a person is born with an extra chromosome. This can affect how their brain and body develop. People diagnosed with Down syndrome can lead healthy lives with supportive care. Down syndrome is a condition in which a person has an extra copy of chromosome 21. Down syndrome occurs when an individual has a full or partial extra copy of chromosome 21. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes the characteristics associated with Down syndrome.
Down syndrome occurs when an individual has a full or partial extra copy of chromosome 21. This additional genetic material alters the course of development and causes the characteristics associated with Down syndrome.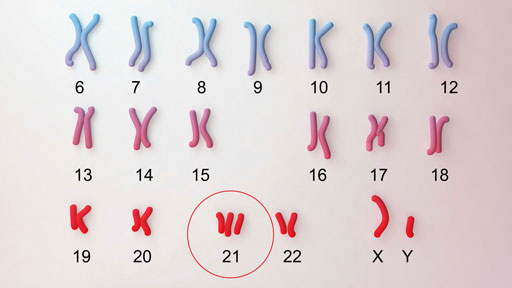 Down syndrome can be diagnosed in infancy based on the characteristic clinical findings. When Down syndrome is suspected in a person, a genetic test called a chromosome analysis is performed on a blood or skin sample to look for an extra chromosome 21 (trisomy 21).
Down syndrome can be diagnosed in infancy based on the characteristic clinical findings. When Down syndrome is suspected in a person, a genetic test called a chromosome analysis is performed on a blood or skin sample to look for an extra chromosome 21 (trisomy 21).